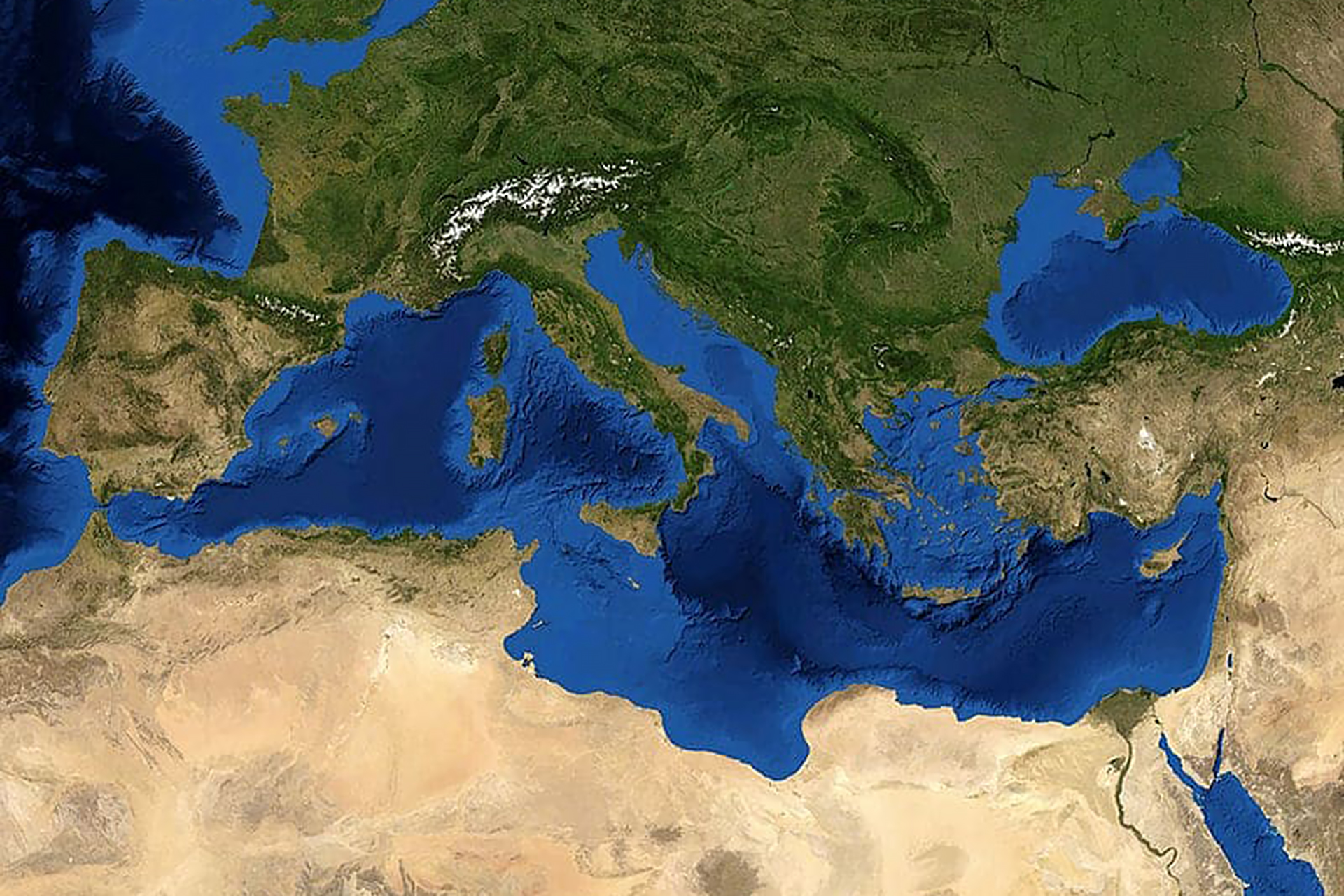
The risks are also compounded by the fact that the Mediterranean is relatively small and enclosed, meaning any tsunami could spread across the basin, home to more than 130 million people.
A new study has revealed that earthquakes in the western Mediterranean basin are more likely to trigger catastrophic tsunamis than scientists previously expected.
The researchers, who for the first time determined the location of the boundary separating the African and Eurasian plates west of the Mediterranean, confirmed that this new discovery increases the likelihood of catastrophic disasters of this type, which scientists expected the Mediterranean to witness. Among them over the next three decades.
Geologically active regions
The Mediterranean Sea is one of the geologically active regions resulting from the collision of the African plate with the western part of the Eurasian plate. About 65 million years ago, this continued collision led to the formation of the Alps and the shrinking of the Mediterranean, during which the African plate continued to move northward at about 2.5 cm per year and sank under the European plate. Seismic and volcanic activity.
Although the geological structure beneath the Mediterranean surface has been extensively studied, the data available so far are insufficient for some regions to accurately know the boundaries between the two plates and to understand the tectonic activity around them.
Accordingly Press release Published on the 23rd of last month by the Institute of Marine Sciences (Institut de Ciències del Mar) in Barcelona, New Science Paper – published recently in the journal Nature Communications – identified for the first time the complex geometry of the active fault system beneath the surface of the Alboran Basin, located in the western Mediterranean between the Moroccan, Algerian and Spanish coasts, and described how it moved. For the last 5 million years.
The accuracy of the data based on the study enabled detailed characterization of the active fault system extending over 300 km, and the results show that fault systems in this region absorb most of the collision-induced deformation. Eurasian and African plates.
The researchers assessed the study’s findings as essential to reassessing the risks of earthquakes and tsunamis affecting coastal areas in the western Mediterranean, especially since previous studies of earthquake and tsunami risks did not take into account the importance of faults under the Alboran Sea. Due to lack of data.

Tsunami Waves in Mediterranean History
Historically, the Mediterranean has witnessed many violent tsunami events, most of them caused by strong earthquakes and landslides along fault systems along the boundaries between the African and Eurasian plates.
It has been nearly a century since Europe’s last major tsunami, a 13-metre-high wave that killed nearly 2,000 people deep in the Mediterranean off the coast of Sicily in 1908.
But tsunami waves in the Mediterranean could be more destructive, according to an article published on the site by Matthew Blackett, professor of physical geography and natural hazards at Coventry University in Britain.Greek reporter“(Greek reporter).
About 3,500 years ago a large volcanic eruption on the island of Santorini caused a wave that completely destroyed the Minoan civilization, an event that may have led to the emergence of the myth of the disappearance of the Atlantis civilization.
A series of magnitude 8.5 earthquakes also occurred off the coast of Crete in AD 365. Some ancient cities in Greece, Italy and Egypt were destroyed by tsunami waves, and 5,000 people died in Alexandria alone.
As for the western Mediterranean, not far from the Alboran Basin, which was included in the last study, the last tsunami in the region dates back to 2003. A strong earthquake was felt in the Boumardez region on the Algerian coast This led to the emergence of tsunami waves that reached a height of about two meters and damaged the beaches of the Spanish Balearic Islands, located about 300 km north of the epicenter.
What about the future?
According to reports published by the newspaper,Guardian“(The Guardian) quoting experts from UNESCO, before the results of the latest study are published, there is a risk of a large tsunami in the next 30 years, during which the one meter high waves will exceed almost 100%. These waves are likely to occur. Reaching the large cities of the Mediterranean coast, such as Marseille, Alexandria and Istanbul. .
Scientists expect rising sea levels to increase the risk of tsunamis in the Mediterranean. A scientific study has shown that a rise in sea level of 45 cm will double the risk of flooding resulting from inundation of up to two and a half meters of seawater on land.
According to Blackett, the risks are also heightened by the fact that the Mediterranean is relatively small and enclosed, meaning that any tsunami could spread throughout the basin, home to more than 130 million people. The warning time required to reduce accidents will also be less.
According to the Guardian, thanks to an early warning system that UNESCO has been focusing on since 2004, all threatened residential communities will be ready to deal with such events by 2030.
Because the risks revealed by the new study are not taken into account, it is possible that the supervisors of the warning system will be forced to reconsider the list of residential communities that are definitely threatened by tsunami waves.

Prone to fits of apathy. Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Internet advocate. Avid travel enthusiast. Entrepreneur. Music expert.