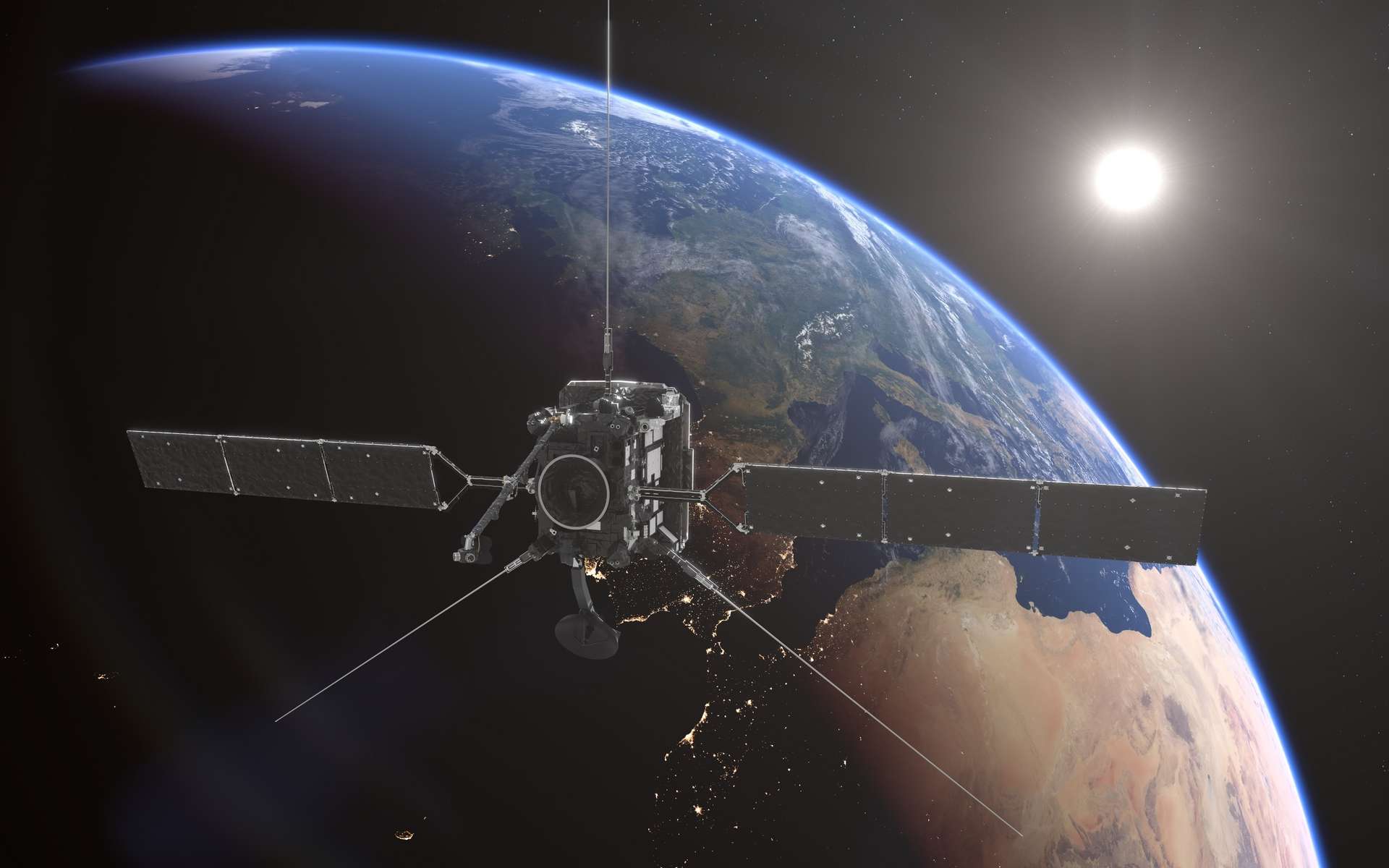
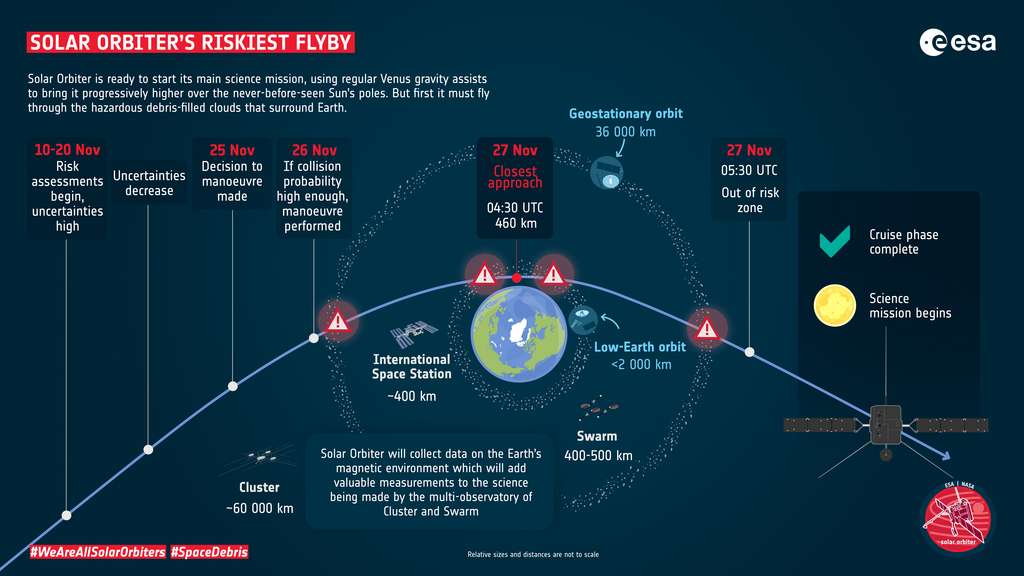
November 27, Solar Orbiter It will fly over the Earth before its main scientific mission begins. Passing at an altitude of only 460 km, the spacecraft will have to overcome the clouds of space debris orbiting our planet, which will turn this plot into the most dangerous overflight ever for a scientific mission.
You might be interested too
[EN VIDÉO] Discover unusual images of the sun using the Solar Orbiter The first images of ESA’s Solar Orbiter have just been released! They reveal the sun in all its glory in the highest definition.
Solar Orbiter Come back to visit us Before embarking on its main scientific mission: Explore the Sun, “” Space weather “. Of course, the investigation Will fly over the ground November 27, passing at 4:30 p.m. UTC (5:30 am Paris time) Only 460 km from North Africa and the Canary Islands. By comparison, the International Space Station The current orbit is 420 km above sea level.
This strategy is needed to reduceEnergy Guide the spacecraft to its nearest point to the Sun. Occasionally Flyover Of our planet, Solar Orbiter But will have to cross Two areas Orbits Populated Space debris : Orbit of geostationary satellites at a distance of 36,000 km and area of objects Orbit Low, about 400 km. Therefore, there is a weakness Risk of collision. Operation Team Solar Orbiter The situation is being monitored very closely, otherwise the course of the investigation will change It seems to be in danger.
Phases of the Earth’s overpass Solar Orbiter November 27, 2021 © ESA
Opportunity in Earth Sciences
This review provides a unique opportunity to learn Earth’s magnetic field. This is a topic of interest, because Magnetic field Is the interface between us Atmosphere And solar wind. The other two missions of study these interactionsThis : The four moons of the mission ClusterAt an altitude of 60,000 km, three moons Group, 400 km. Many spacecraft are needed to break the “space-time ambiguity”, that is, the uncertainty as to whether a change occurred because a spacecraft moved from one area to another under different conditions (change in space) or flew over an exploration. Area with changing circumstances (change of time). Review of Solar Orbiter Additional data points will be provided to reconstruct the condition and behavior of Earth’s magnetic field.
The cruise phase is complete
This review marks an important stage in the investigation. Off Its launch in February 2020 Until July of the same year Solar Orbiter It was in the commissioning phase, during which scientists and engineers tested the spacecraft and its equipment. From July 2020, Solar Orbiter The cruising stage is over. Meanwhile, the tools In place The measurements of are taken Solar wind In addition to other conditions surrounding the probe, the remote sensing devices designed to look at the sun were characterized by their advanced calibration and characterization.
That’s good Solar Orbiter Not yet in full scientific mode, a lot of scientific data has been produced. Daniel Mുള്ളller, project scientist Solar Orbiter, Explains an upgrade of ESA Ground Station Network The mission allowed more data to be sent to Earth than expected, and the scientists on the mission quickly benefited: more than fifty articles describing the scientific effects of the cruise phase. Solar Orbiter The journal should be published in December Astronomy and astronomy.
The Solar Orbiter will fly over the Earth, which would be a dangerous ploy because it would have to overcome the clouds of space debris orbiting our planet. © European Space Agency, This
Close to the sun
The first perihelion of the solar orbiter In June 2020, it occurred at a distance of 77 million km from the Sun. By March 2022, the inquiry will be as close as possible to its second pass Star, This time less than 50 million kilometers. ” This will be one-third The distance between the sun and the earth, Explains Daniel Mുള്ളller. So, when compared to all the high pictures Resolution What we have already achieved, everything will now be doubled This includes new views of ‘ Campfire Puzzle Solar Orbiter Observed in his first time Perihelion.
Solar Orbiter Do not approach Very close to the sun That is the investigation Parker Solar Probe From NASA, But it is voluntary: it is not only allowed Solar Orbiter To measure what is happening in the solar wind, but also to carry telescopes that can look at the sun Without being destroyedThe With heat. The two data sets can then be compared to the activity on the surface of the sun Weather forecast Spatial around the probe.
Observation challenge
In the moments before the path approaching the Earth, observers Canaries et en North Africa The spacecraft can be briefly seen floating in the sky. It moves at about 0.3 degrees per second, which is more than half the visible diameter The moon Every second. For most observers, it will be too dim to seeEye Naked and too fast for telescopes to follow. So binoculars should give you the best chance of seeing it.
when Solar Orbiter It will rise from the shadow of the earth and go to a meeting with the sun and the never-before-seen solar poles. The scientific phase of this great mission will begin.
What you need to remember
- November 27 at 4:30 am UTC (5:30 am PST), Solar Orbiter It flies overland at an altitude of 460 km above North Africa and the Canary Islands.
- The probe will provide an opportunity to study the Earth’s magnetic field.
- It will then embark on its main scientific mission: to explore the Sun and its relationship to “space climate”.
- In March 2022, the spacecraft will orbit its second orbit closer to our star.
—
The future in the stars, This is an unavoidable getaway for those who love astronomy and space. Every month, for a complete tour of the month’s ephemeris, meet us with advice on how to better observe what is happening in the sky. A special episode published on the 15th of each month invites you to learn more about a particular object or event that marks astronomy and space news.
—
Interested in what you just read?

Prone to fits of apathy. Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Internet advocate. Avid travel enthusiast. Entrepreneur. Music expert.