A catastrophe rocked Europe 34 million years ago: the massive extinction of the world’s most populous species. This event is known as Great break, Or Great Bankruptcy, and the sudden change in temperature and pressure exerted by Asian species on endemic species, scientists have so far considered. Theories that strengthen Recent discovery Of a lost territory Under the waters of the Aegean and Adriatic seas It would connect the Balkans and the Anatolian Peninsula and facilitate transportation from Asia to Europe.
Because the continent is bordered by two continents, the continent, baptized exactly as the Balkanatolia, would have risen and sank during the Eocene 56 to 34 million years ago. Occasionally a large island or archipelago is formed.
With the end of the Eocene, a sharp drop in temperature will cause sea levels and avalanches to drop.Or it could have become a bridge between Asia and Europe For a long time. Researchers say that this could lead to the migration of all Asian species, from rhinos to hamsters, to the southern hemisphere.
The theory was developed by a team of French, American, and Turkish geologists and paleontologists after their discovery of mammalian fossils in Turkey 38 to 35 million years ago. Clear Asian morphologyThe first remnants of these characteristics have so far been found in the area.
Following that discovery, they reviewed paleontological discoveries made along the Aegean and Adriatic coasts from the 19th century onwards, finding that the Anatolia and the Balkans were home to a large variety of eocene endemic species. From other parts of Europe and East Asia that led them Raise the theory of Balkanatolia, a large island in betweenAccording to the French National Center for Scientific Research.
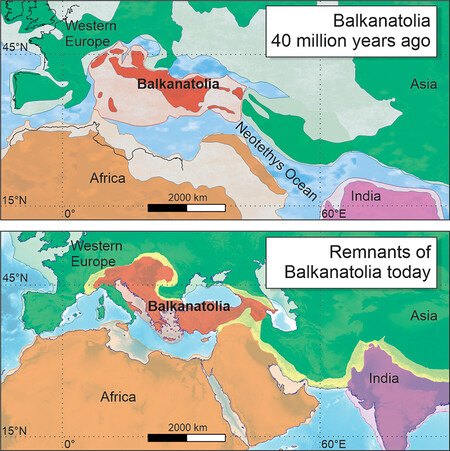
Balkanatolia Map | National Center for Scientific Research in France.
In that review, the authors of the study found that previous research had documented the findings of mammalian remains close to Asian species in Italy or the Balkans. 10 million years before the Grande Cooper occurred.
All of this led them to conclude that Balkanatolia was an isolated island or group of islands in a large part of the Eocene, which is home to a variety of spontaneous fauna from Europe and Asia. At the end of that underground age, the planet’s cold caused the water to dwindle and freeze in some places. Asian species were first allowed to reach the BalkanatoliaLater, when the temperature drops further, the Grande Cooper begins, as shown by the fossil remains found in Turkey, the Balkans, and Italy.
Picture | Christian Palmer

Prone to fits of apathy. Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Internet advocate. Avid travel enthusiast. Entrepreneur. Music expert.



