The announcement was made at a press conference on Thursday, May 12 at 4 pm (Romanian time) in Washington by NFS Chief Operations Officer Karen Marongelle.
The other four researchers are required to provide details about the scientific discovery.
Michael Johnson, astronomer at the Center for Astrophysics (Harvard & Smithsonian), Katy L., Professor of Computer Science, Mathematics, Electrical Engineering and Astronomy. Bowman (Caltech), Vincent Fish, Researcher (MIT Hostock Observatory) Ferial Osel, Professel. Department of Astronomy and Physics (University of Arizona).
Simultaneous press conferences on the same subject will be held in Munich, Shanghai, Mexico City, Santiago de Chile, Tokyo and Taipei.
Streaming linkPress conference leads to a page dedicated to black holes in the universe.
Black holes are extremely dense formations, and because of their high gravitational pull, no electromagnetic radiation – including light – can escape such a trap.
They predicted Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity, according to which a sufficiently compact mass would distort the spatio-temporal continuum and create a black hole.
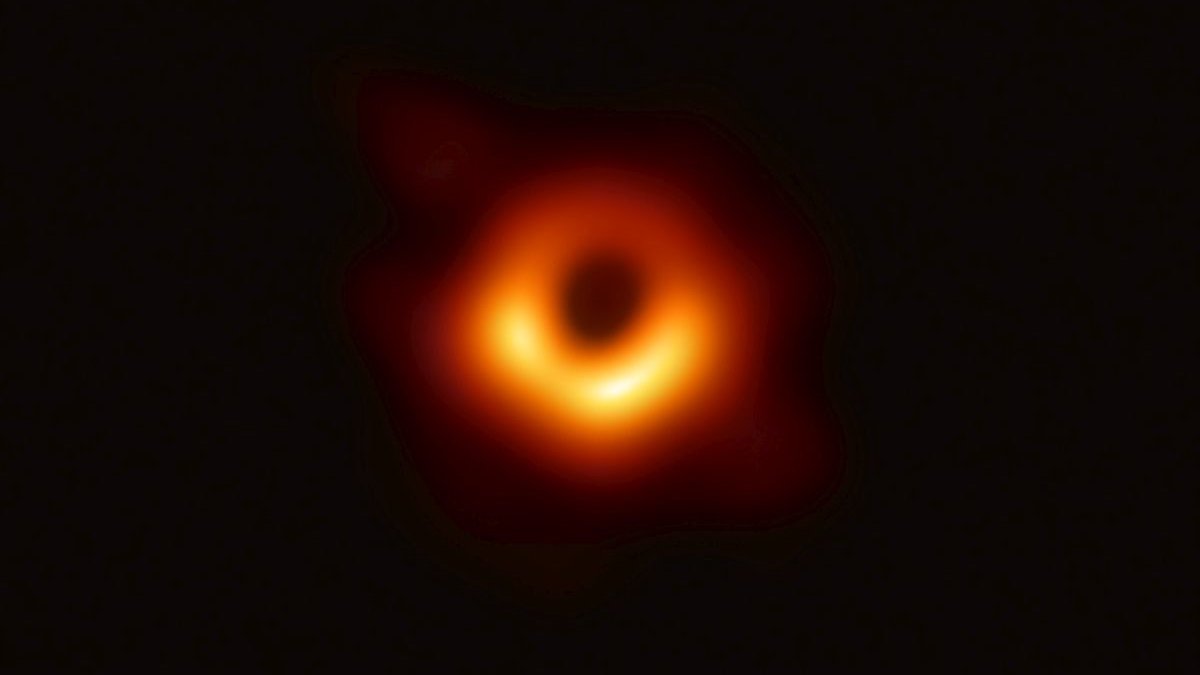
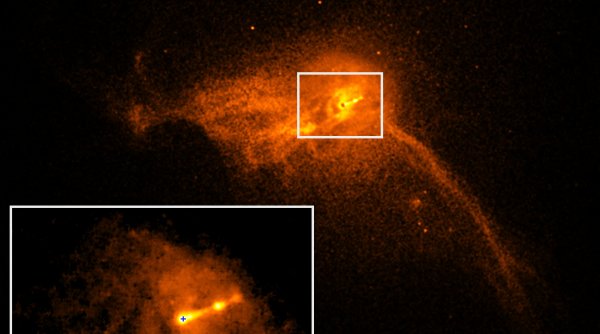
According to the NSF, the first image of a supermassive black hole was made in 2019 Event HorizonNamed for a series of terrestrial radio telescopes interconnected on a planetary scale.
The image reveals that this formation is located in the center of the galaxy Messier 87, which is located in the constellation of Virgo.
Photo (Main and Gallery): Image of the super-massive black hole in the Galaxy Messier 87 by Event Horizon

Prone to fits of apathy. Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Internet advocate. Avid travel enthusiast. Entrepreneur. Music expert.