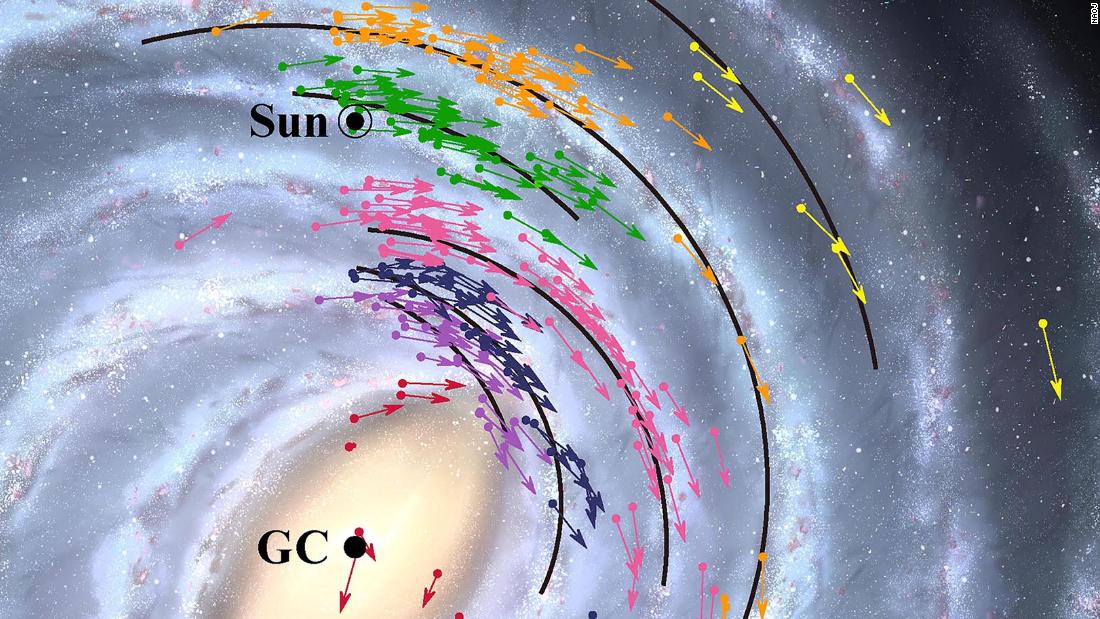
This map suggests that the center of the Milky Way and the black hole that sits there are 25,800 light-years from Earth. According to the National Observatory for Japan, the value of the 27,700 light-years accepted by the International Astronomical Union in 1985 is very close to the official value.
What’s more, our solar system orbits the center of the galaxy at a speed of 227 kilometers per second – which is faster than the actual value of 220 kilometers per second.
Because Earth is located within the Milky Way, it is difficult to go back and see what the galaxy looks like. To overcome this, project astronomy accurately measures the position and motion of objects to understand the overall structure of the Milky Way and the position of the Earth in it.
A more precise approach
In August, Vera published its first catalog, which contained data on 99 celestial objects. Based on this catalog and recent observations from other groups, astronomers have developed a position and speed map. From this map, scientists have been able to calculate the center of the galaxy, and everything revolves around it.
Vera integrates data from four radio telescopes across Japan. When combined, astronomers can also find an American penny placed on the lunar surface in theory that telescopes could achieve a resolution.
Clearly, that does not mean the Earth is falling into a black hole, the observatory said. On the contrary, the map more accurately identifies the location of the solar system.

Prone to fits of apathy. Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Internet advocate. Avid travel enthusiast. Entrepreneur. Music expert.