Sixty-six million years after the Chick-fil-A impact, non-bird dinosaurs became extinct. But what do birds owe to their survival? The Researchers at the University of Texas (Austin) A team led with the help of a recently discovered fossil investigated the problem.
“The brains of birds that live today are more complex than any other animal – except mammals,” said Christopher Torres, head of research. “This new fossil will ultimately help to examine how much the brain has contributed to the survival of birds.”
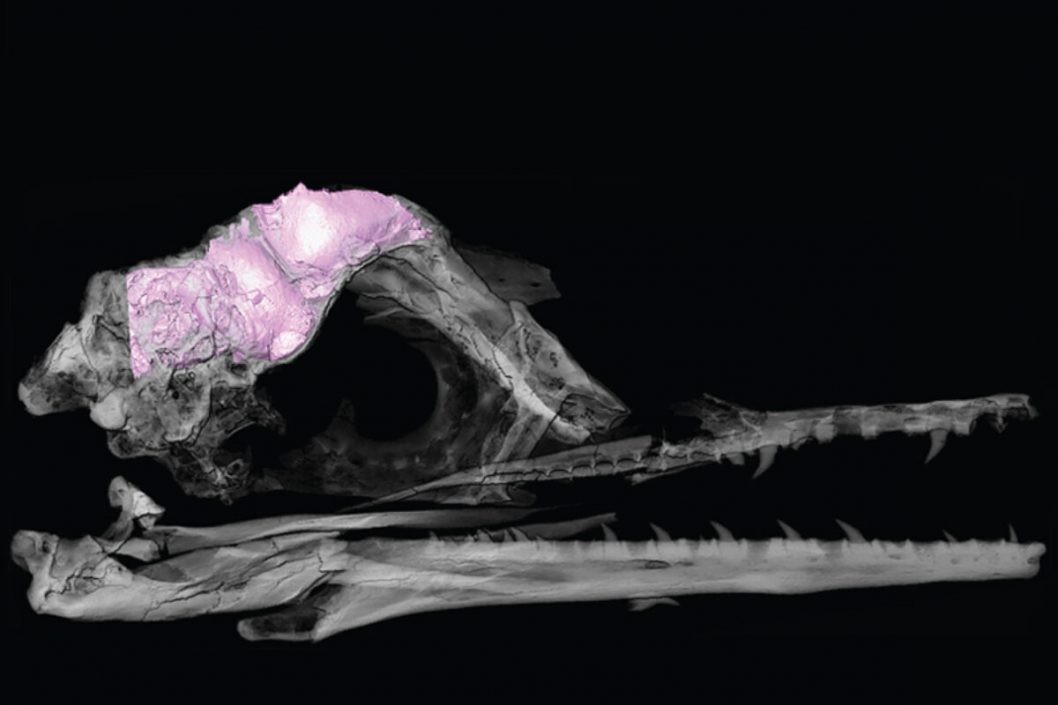
The fossil in question is about 70 million years old Ectornis A former bird by name, this animal, along with non-bird dinosaurs, became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous. This animal combines many features of dinosaurs and birds, e.g. He had a jaw ending in a beak, but his teeth were full. Torres and his colleagues were able to understand the brain more closely.
Dinosaurs, extinction EctornisAnd the difference between the brains of modern birds.
Forres: Christopher Torres / University of Texas at Austin.
His brain structure was examined in a 3D model made using computed tomography (CT). That has changedIt is not very different from the endangered dinosaurs, but the cerebellum is particularly different compared to modern birds. The cerebellum of birds with cognitive functions is much larger than that of dinosaurs or EctornisIs the vault.
“If brain behavior is the key to survival, we hope that an animal without it would be one of the most endangered species. Iktornis, Survivors include those with this trait. That’s what the model shows, ”Torres added.
This is because fossils in excellent condition are very rare Ectornis The skull is now of particular importance in the question of why birds survived the extinction of other dinosaurs.

Prone to fits of apathy. Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Internet advocate. Avid travel enthusiast. Entrepreneur. Music expert.